Part:BBa_K1499001
wssG gene
This part encodes wssG, a gene found in the wss operon of Pseudomonas fluorescens theorized to be involved in the acetylation of cellulose.
Usage and Biology
wssG is one of the four genes isolated from Pseudomonas fluorescens responsible for acetylating cellulose (the others being wssFHI, K149000, 2, 3). The wss operon in P. fluorescens contains 10 genes responsible for biofilm production, allowing the bacterium to colonize the air-liquid interface. The operon includes genes necessary for the biosynthesis of cellulose (including many with homologies to E. coli or G. hansenii, including minD, subunits of cellulose synthase, and a cellulose), and four (wssF-I) have been implicated as responsible for the acetylation of the cellulose polymer. wssG has been purported to form an acetylation complex associated with cellulose synthase [1].
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 570
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
Verification
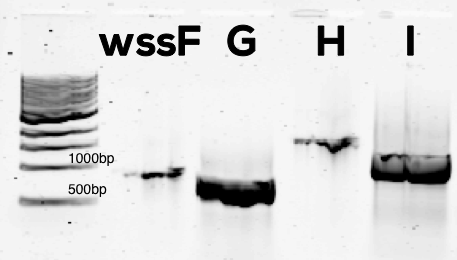
We successful isolated the four acetylation genes from P. fluorescens total DNA (Figure 1).
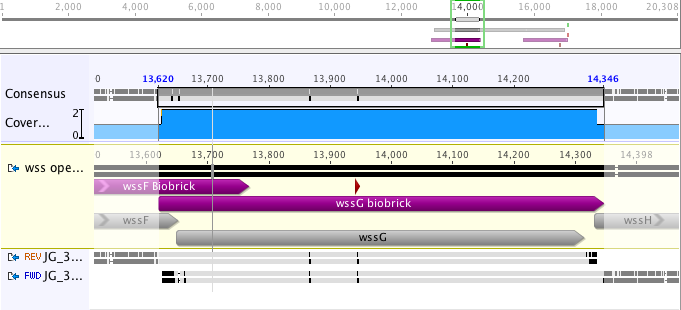
The part sequence contained BioBrick restriction sites, which had to be removed before sequencing (see Design Page). The part was sequence verified after insertion into pSB1C3 and before submission to the registry with two reads using VF2 and VR (Figure 2).
Results
This part has been successfully cloned into the BioBrick backbone, but for expression in G. hansenii, our model cellulose-producing organism, we needed to use the multi-host shuttle vector pUCD4 (Figure 3).
This procedure was more time-consuming than expected, as the pUCD4 plasmid is >10kb, the maximum size able to be purified by spin columns. Further work is needed to prove the activity of the wss genes in acetylating cellulose.
References
[1] Spiers AJ et al. (2013) Cellulose Expression in Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25 and Other Environmental Pseudomonads in Cellulose - Medical, Pharmaceutical, and Electronic Applications. DOI: [http://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfs-wm/45637.pdf 10.5772/53736]
| None |